Everything You Need to Know
About UPS Systems
A Practical Guide to Choosing the Right One
In today’s world, electricity powers everything—from small homes to massive factories and hospitals. A sudden blackout or unstable voltage can mean lost data, damaged equipment, or halted production. This is where a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) becomes essential: it ensures your devices keep running smoothly and shields them from electrical problems.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to understand UPS systems, the differences between types, and what to consider when choosing the right one. We’ll also explain why buying certified UPS devices from trusted suppliers like EGTRADE is the smartest way to protect your home, business, or critical equipment.
What is a UPS and Why Do You Need It?
Unexpected power outages or voltage fluctuations can cause serious issues—whether at home, in the office, in factories, or even in hospitals. That’s where a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) comes in.
A UPS provides an instant backup power source the moment electricity goes down, protecting your devices from damage and preventing data loss.

Not a Generator!
Unlike a generator, a UPS doesn’t produce electricity for hours. Instead, it provides instant backup power for a limited time, along with voltage regulation and surge protection—enough to safely shut down your devices or keep them running until a generator kicks in.
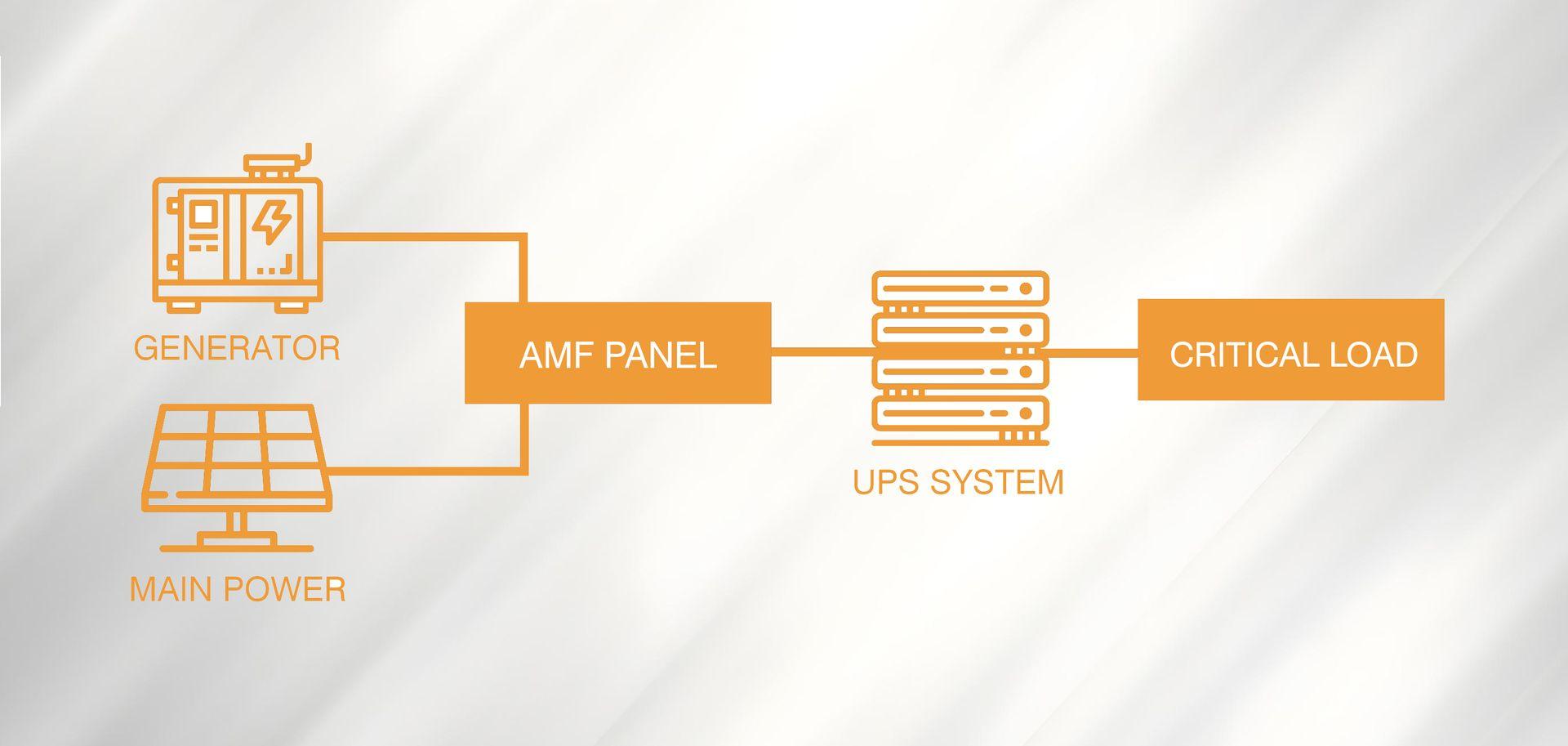
How Does a UPS Work?
Online (Double Conversion)
virtually zero transfer time since the inverter is always active
Line-Interactive
faster switching, adds voltage regulation
Offline / Standby
a few milliseconds delay
Transfer time depends on the UPS type:
Rectifier/Charger & Battery
The rectifier/charger keeps the batteries charged and conditions the power, while the batteries act as the backup energy source during outages.
Inverter
converts DC battery power into clean AC power.
Static Bypass
an emergency path that keeps loads running in rare fault conditions
Every UPS typically includes:
UPS Operating Scenarios
To better understand how a UPS protects your equipment,
let’s look at how it behaves under different situations:
If the UPS itself develops a fault or requires maintenance, the static bypass automatically activates. This instantly transfers the load back
to the main utility power
(bypass line) to ensure there is no break in supply.
This feature guarantees continuous power even during UPS failures or servicing.
If the grid fails or voltage goes out of tolerance, the inverter immediately switches to draw power from the batteries. The output remains stable, so connected equipment continues running without interruption. The backup time depends on the battery capacity and the load being powered. Once utility power is restored, the rectifier takes over again, recharging the batteries.
Operation
When utility power is stable, electricity passes through the rectifier, which converts AC to DC. Part of this energy charges the battery, while the rest is sent to the inverter, which converts it back to AC and supplies clean power to connected devices.
Types of UPS Systems
UPS systems come in different designs to match various needs.
Here are the three main types and their best use cases:
Online UPS (Double Conversion)
- Continuously converts AC→DC→AC, delivering clean, stable power.
- Offers the highest protection with almost zero transfer time.
- Best for: hospitals, data centers, factories,
and mission-critical servers.
Line-Interactive UPS
- Features an Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)
to handle minor surges or drops without draining
the battery. - Best for: small-to-medium offices, network equipment, DVRs, and CCTV systems.
Offline / Standby UPS
- The simplest and most
affordable type. - Switches to battery only when the main power fails.
- Best for: home PCs, printers, routers, and small devices.
Hotels
Ensures uninterrupted operation of front-desk systems, cameras, and online booking
systems—protecting guest comfort and
the hotel’s reputation.
Homes
Keeps your computer, router, TV, or even a small fridge safe from sudden shutdowns, preventing data loss and hardware damage.
Companies
Keeps essential office equipment, servers, and communication systems running during outages—maintaining productivity and avoiding costly downtime.
Hospitals
Absolutely critical for sensitive life-support equipment like ventilators and ICU systems—where power loss can mean loss
of life.
Why UPS Matters in Different Sectors?
Factories
Protects production lines and heavy machinery from unexpected stops, reducing costly breakdowns and downtime.
Single-Phase vs Three-Phase UPS
Single-Phase (0.5–20 kVA)
10–20 kVA → light medical equipment.
and data centers.
Efficiency
Applications
500+ kVA → heavy manufacturing, critical infrastructure.
Three-Phase (10–1000+ kVA)
Applications
small/medium offices, clinics.
less power-hungry.
Efficiency
How to Choose the Right UPS
The right UPS depends on your needs. Regular users should size their load, add a safety margin, and choose the right runtime. Engineers and IT managers must also consider advanced specs like power factor, scalability, and monitoring. Always avoid undersizing or ignoring runtime.

A) For Regular Users
- Calculate your load (W): Convert to VA → VA ≈ W ÷ Power Factor (pf)
(if unknown, assume pf = 0.7–0.8).
- Add a safety margin: Always choose a UPS with 20–30% more
capacity than your total load.
- Decide on runtime: How long do you need backup?
(e.g., 10–15 mins to shut down safely).
- Pick the right topology: Line-Interactive for home/office use;
Online for highly sensitive equipment.
(if unknown, assume pf = 0.7–0.8).
capacity than your total load.
(e.g., 10–15 mins to shut down safely).
Online for highly sensitive equipment.
Example
PC (300W) + Monitor (60W) + Router (20W) = 380W.
With pf=0.8 → 475 VA.
Add 30% margin → ~650 VA.
So, choose a 700–1000 VA UPS for comfort.
B) For Engineers & IT Managers
- Topology:
- Normal office with moderate fluctuations → Line-Interactive.
- Mission-critical or zero-downtime environments → Online
(Double Conversion).
- Key Specs to Check:
- Capacity (kVA) with Power Factor (0.9 recommended).
- Low Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) output.
- Crest factor for devices with high inrush currents.
- Scalability (modular, N+1 redundancy).
- Monitoring & control (USB/SNMP).
- Battery type (VRLA vs. Li-ion), lifespan, and temperature ratings.
- Compliance with medical/industrial standards.
(Double Conversion).
C) Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Buying a UPS too close to your actual load (no margin).
- Ignoring required runtime.
- Forgetting startup/inrush currents of some devices.
- Overlooking environmental conditions (heat, dust, ventilation).
Explore UPS Solutions
The right UPS can save you downtime
Conclusion
A UPS is not a luxury—it’s an essential layer of protection for your devices and operations.
Line-Interactive UPS covers most home and office needs.
Online (Double Conversion) UPS is the gold standard for hospitals, factories, and data centers.

Choose wisely based on your load, required protection, and runtime needs—then relax knowing your systems are safe.
If you’re not sure which UPS is right for your home, business, or project, our team at EGTRADE is here to help.
Contact us today and let us guide you to the best solution that fits your needs.
Our latest content
Check out what's new in our company !
Related Keywords
uninterruptible power supply Egypt, best UPS for home, online UPS vs line interactive, UPS for hospitals, UPS for factories, UPS backup time, UPS capacity calculation, power outages protection, reliable UPS brands Egypt, modular UPS systems, VRLA vs lithium UPS battery, UPS for IT managers, data center UPS solutions, mission critical UPS Egypt, crest factor UPS, low THD UPS, industrial UPS supplier Egypt, hospital UPS backup, office UPS systems, EGTRADE UPS solutions, UPS installation guide Egypt, how to choose UPS, UPS runtime calculation, UPS maintenance Egypt, safe power backup